In statics, Lami's theorem is an equation that relates the magnitudes of three coplanar, concurrent and non-collinear forces, that keeps a body in static equilibrium.
Lami’s theorem states that if three forces acting at a point are in equilibrium, each force is proportional to the sine of the angle between the other two forces.
Consider three forces A, B, C acting on a particle or rigid body making angles α, β and γ with each other.
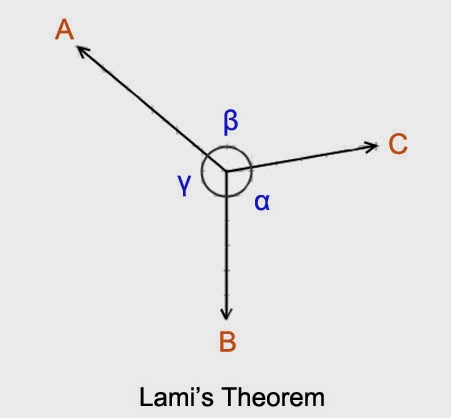
According to Lami’s theorem , the particle shall be in equilibrium if
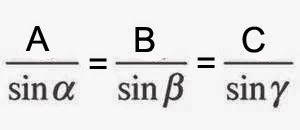
The angle between the force vectors is taken when all the three vectors are emerging from the particle.
No comments:
Post a Comment